Discover Key Principles of Sustainable Building Design
- indrsarv
- Oct 31, 2025
- 4 min read
Sustainable building design is transforming the way we think about construction and architecture. It focuses on creating structures that are environmentally responsible, resource-efficient, and healthy for occupants. This approach not only reduces the environmental footprint but also enhances the quality of life for those who live and work in these buildings. By integrating eco-friendly building strategies, we can build smarter, greener, and more resilient spaces for the future.
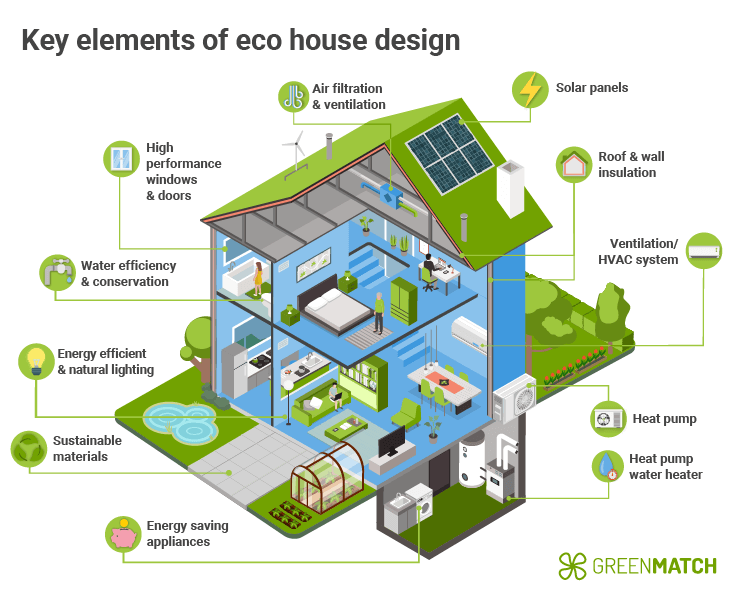
Understanding Eco-Friendly Building Strategies
Eco-friendly building strategies are essential for reducing the impact of construction on the environment. These strategies involve using materials, technologies, and design principles that conserve resources and minimise waste. Some common approaches include:
Energy efficiency: Using insulation, energy-efficient windows, and renewable energy sources like solar panels.
Water conservation: Installing low-flow fixtures, rainwater harvesting systems, and greywater recycling.
Sustainable materials: Choosing recycled, locally sourced, or rapidly renewable materials.
Indoor environmental quality: Ensuring good ventilation, natural lighting, and non-toxic finishes.
For example, a building designed with high-performance insulation and triple-glazed windows can significantly reduce heating and cooling needs. Similarly, incorporating green roofs or walls can improve insulation and reduce urban heat island effects.
These strategies not only reduce operational costs but also contribute to healthier living
environments. Implementing them requires careful planning and collaboration between architects, engineers, and builders.
What are the 6 R's of sustainable design?
The 6 R's of sustainable design provide a framework for reducing environmental impact throughout a building's lifecycle. They are:
Reduce - Minimise the use of materials and energy during construction and operation.
Reuse - Incorporate existing materials or components to avoid waste.
Recycle - Use recycled materials and ensure waste is recycled after demolition.
Rethink - Challenge traditional design methods to find innovative, sustainable solutions.
Refuse - Avoid materials and practices that are harmful to the environment.
Repair - Design buildings that can be easily maintained and repaired to extend their lifespan.
For instance, reusing bricks from a demolished building reduces the need for new materials and lowers landfill waste. Rethinking design might involve orienting a building to maximise natural light and ventilation, reducing reliance on artificial systems.
These principles encourage a holistic approach to sustainability, ensuring that every stage of a building’s life is considered.
Integrating Renewable Energy in Building Design
One of the most impactful eco-friendly building strategies is the integration of renewable energy systems. Solar panels, wind turbines, and geothermal heating can drastically reduce a building’s carbon footprint.
Solar energy is particularly popular due to its scalability and decreasing costs. Installing photovoltaic panels on rooftops or facades can generate electricity to power lighting, heating, and appliances. Additionally, solar water heaters can provide hot water efficiently.
Wind turbines can be effective in areas with consistent wind patterns, while geothermal systems use the earth’s stable temperature to heat and cool buildings with minimal energy.

To maximise benefits, renewable energy systems should be integrated early in the design process. This allows for optimal placement and sizing, ensuring the building meets its energy needs sustainably.
Water Efficiency and Sustainable Landscaping
Water conservation is a critical aspect of sustainable building design. Buildings consume large amounts of water for daily activities, landscaping, and cooling systems. Implementing water-efficient technologies and landscaping can significantly reduce this demand.
Low-flow faucets, dual-flush toilets, and water-efficient irrigation systems help minimise water use indoors and outdoors. Rainwater harvesting systems collect and store rainwater for non-potable uses such as irrigation and toilet flushing.
Sustainable landscaping involves selecting native or drought-tolerant plants that require less water and maintenance. Using permeable paving materials allows rainwater to infiltrate the ground, reducing runoff and replenishing groundwater.
For example, a building with a rain garden can capture and filter stormwater, improving water quality and reducing flooding risks.

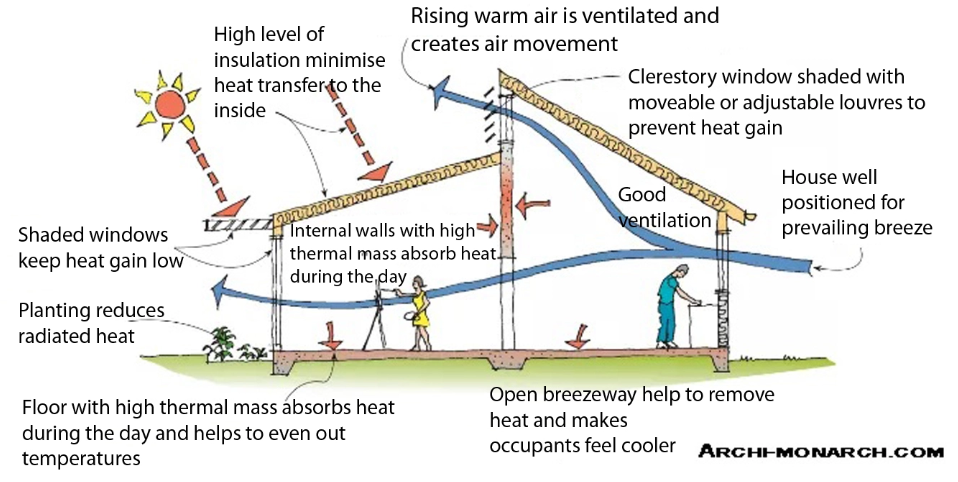
Enhancing Indoor Environmental Quality
Creating healthy indoor environments is a key goal of sustainable building design. Good indoor environmental quality (IEQ) improves occupant comfort, productivity, and well-being.
Natural ventilation and daylighting reduce the need for artificial lighting and mechanical cooling. Using non-toxic paints, adhesives, and finishes prevents indoor air pollution. Proper ventilation systems remove contaminants and maintain fresh air circulation.
Acoustic design also plays a role in IEQ by minimising noise pollution, which can affect concentration and stress levels.
Designers can incorporate operable windows, skylights, and light shelves to enhance natural light and airflow. Selecting materials with low volatile organic compounds (VOCs) ensures healthier indoor air.
Moving Forward with Sustainable Building Design
Adopting sustainable building design principles is no longer optional but necessary for a resilient future. By embracing eco-friendly building strategies, we can reduce environmental impact, lower operating costs, and create healthier spaces.
Whether you are planning a new construction or retrofitting an existing building, consider these key principles:
Prioritise energy and water efficiency.
Use sustainable and recycled materials.
Integrate renewable energy systems.
Design for durability and adaptability.
Enhance indoor environmental quality.
For inspiration and practical examples, explore projects that showcase sustainable building design in action. These real-world applications demonstrate how thoughtful design can harmonise with nature and meet modern needs.
By making informed choices and collaborating with experts, every building can contribute to a more sustainable and eco-friendly future. Get in touch with us to learn more.




Comments